As Covid-19 cases rise around the world, life has actually ended up being complicated for the numerous parents sending their young, unvaccinated children back to school. Some public health experts are bracing for more break outs of the extremely contagious delta version, even as a number of US states have tried to bar schools from requiring procedures such as mask-wearing, with some keeping in mind that children are at low threat from the virus.
Heres a take a look at lessons found out so far.
Researchers are likewise questioning what the surge implies for kids. Could kidss biology hold ideas for beating the infection? Scientists are beginning to assemble the pieces of biological information and social patterns that might explain why children are mainly spared.
Has Covid been an issue for children?
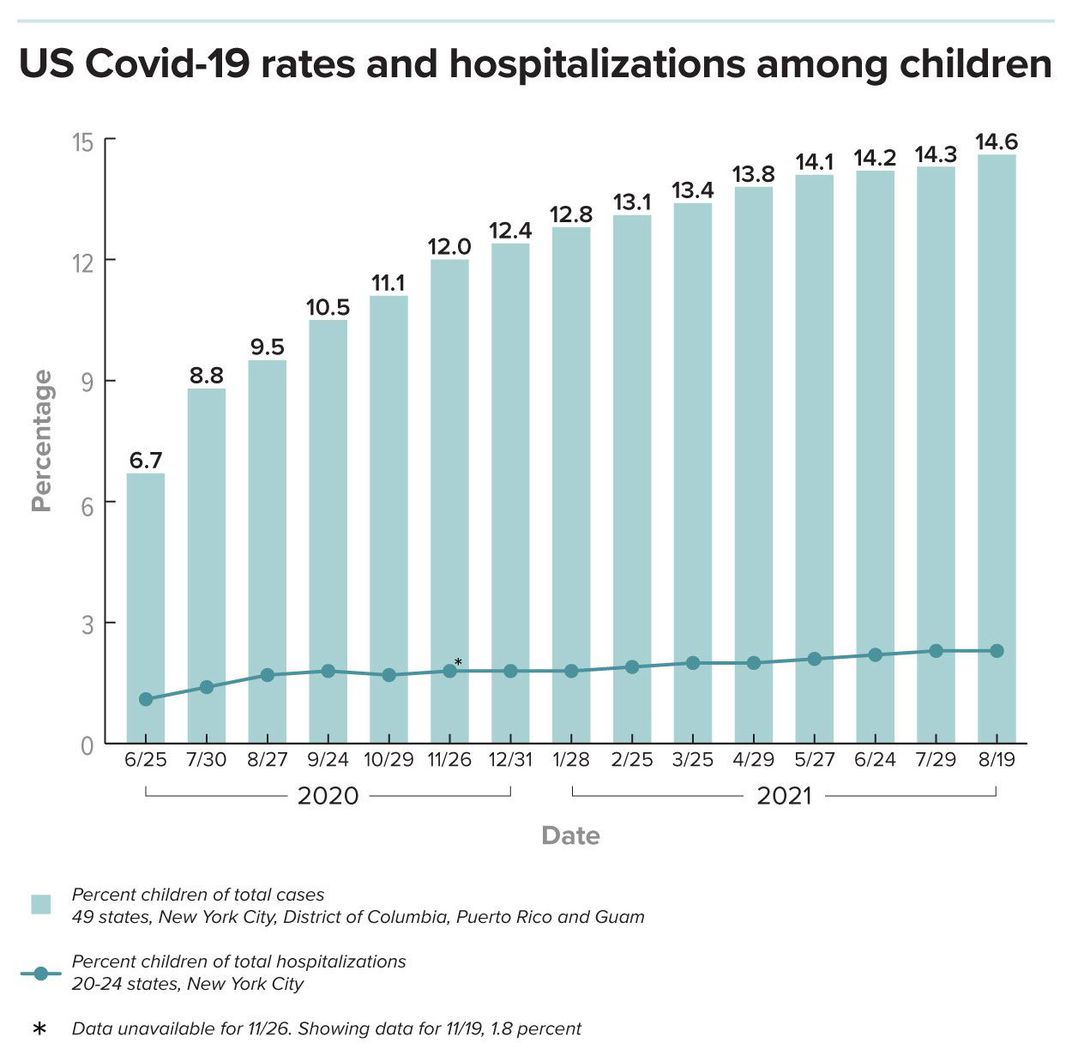
Still, kids have accounted for almost 15 percent of all cases in the US given that the start of the pandemic– and represent a lot more than that today: about 22.4 percent of cases for the week ending August 26. There is no proof yet that the delta variation is more unsafe to kids than previous versions of the virus, but vaccines are not yet offered for kids under 12, many locations have actually loosened public health constraints, and delta is so contagious that it is spreading out quickly. Approximately 350 kids under 18 each day were hospitalized the week of August 24 to August 30, and childrens hospitals in some states have run out of beds.
Overall, kids have been lucky with the pandemic: Although its not yet clear whether they are less most likely than grownups to agreement or transfer Covid-19, they are far less most likely to get ill. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of August 25 just about 400 children under 18 have passed away of the disease in the US. And, of the two lots states reporting in addition to New York City, simply 0.1 percent to 1.9 percent of kids who tested favorable for the infection have actually been hospitalized. A recent UK research study that crowdsourced health info from the public through an app discovered that only 1.8 percent of children with Covid-19 still had signs eight weeks after infection.
Why dont kids get as sick as adults?
( Source: Staff Reporting, Knowable Magazine).
When a totally new pathogen like SARS-CoV-2– the cause of Covid-19– comes along, grownups dont have as lots of naive cells to acknowledge and respond to the brand-new hazard. “For kids, thats all they have,” says immunologist Donna Farber of Columbia University.
A 2020 research study provides assistance to that idea. Tracking a group of adults and kids with Covid-19, it found that the blood of kids and youth under 24 contained greater levels of cytokine proteins called IL-17a and IFN-γ, which instruct the innate immune system to attack. This group also recuperated much more rapidly than the adults.
And a 2021 study from Farbers lab found that kids with Covid-19 produce fewer kinds of antibodies against the virus, and smaller amounts of them than grownups do. Thats probably since they do not require to, she says: The inherent body immune system has currently taken care of the infection.
Part of the explanation for kids resilience might depend on their general health. Kids are less likely to have conditions like obesity and diabetes, which increase the possibility of serious Covid-19.
The flu is more harmful for young kids than for healthy grownups under age 65, as is breathing syncytial virus (RSV). In those cases, the more someone is exposed to the viruses over the course of their lives, the stronger their immune response ends up being.
Children represent a small portion of identified United States Covid-19 cases, as revealed in this chart. But that all-time portion has actually gradually inched up due to an increased proportion of child Covid cases more just recently: In the week ending August 26, 2021, children represented about 22.4 percent of US Covid cases. The chart also shows that hospitalization rates for kids who check positive for the virus are really low.
This table lists a few of the potential reasons that kids do not tend to get as ill as adults from Covid-19.
Still, Farber believes theres a more essential factor why kids are reasonably resistant to SARS-CoV-2. That mopping is done by another branch of the immune system that likewise varies in between old and young: the inherent immune system, which includes cells like macrophages and neutrophils that swallow up foreign intruders and particles.
A significant immunological difference might help to describe these realities. Compared with grownups, kids have more “naive” versions of T cells, which are customized to recognize specific pathogens. By the time a person reaches their 30s, much of these naive cells will have come across pathogens and developed into “memory” T cells that can respond much more quickly need to they encounter that exact same, or comparable, pathogen again.
( Source: Children and Covid-19: State Data Report/ AAP and the Childrens Hospital Association August 19, 2021, Knowable Magazine).
And kidss immune systems are less developed, which may actually supply an advantage. This “cytokine storm” is less common in kids than in adults.
The story may be more complex, however, since childrens immune systems are fundamentally unlike those of grownups, in manner ins which are still under research study. Researchers understand, for example, that the novel coronavirus isnt the only pathogen to show much less damaging to children. Adults tend to get much sicker from diseases like hepatitis and mumps; kids with hepatitis often reveal no symptoms at all.
Do kids actually spread Covid-19 less than grownups?
However the photo might be altering with the highly transmissible delta variant, which reaches levels in samples that are 1,000 times greater than those of the original stress, likely due to much faster replication in the body. “Whatever advantage kids had actually is now overwhelmed by larger infecting dosages,” says Catherine Bennett, an epidemiologist at Deakin University in Australia. Additionally, delta is hitting at a time when lots of locations are unwinding constraints on masks and social distancing. “Everything is changing, and the infection is changing,” she states.
Australia, for example, managed to largely prevent severe Covid-19 break outs until recently. Now, outbreaks of the delta variation in Brisbane and other parts of Queensland appear to be driven by school transmission, for instance at sports satisfies, Bennett states. If delta is replicating quickly in the body, it could reduce the time between when a person is contaminated and when it begins to spread out, making quarantining challenging, she adds. “By the time you find a problem in a school, its currently impacted other schools.”.
And though kids do still spread out the infection, its hard to know how important schools are in that transmission chain. “Its a truly hard question,” says Shamez Ladhani, a pediatric transmittable illness consultant at St. Georges Hospital in London. Its often tough to tell whether schools are sources of outbreaks or merely showing transmission rates in the wider neighborhood.
Far, lots of research studies have actually reported that schools arent a significant source of transmission. For circumstances, from March 2021 to June 2021, Benjamins team followed more than 1 million primary school students and staff at North Carolina schools with mask requirements. Throughout this period, more than 7,000 kids and staff with Covid-19 went to school while infectious and exposed more than 40,000 people, who had to quarantine as a result. When the scientists did contact tracing and testing, they found only 363 cases of Covid-19 transmitted at schools during this period. If mask policies are enforced, Benjamin concludes, schools are amongst the most safe public buildings to be in. A number of other states and countries whose schools remained open during the pandemic program similar patterns.
Transmission by children has been incredibly hard to study, not least due to the fact that numerous kids never ever reveal signs of the virus at all. In theory, kidss smaller, weaker diaphragms would suggest that they do not puff out virus as far when they talk or breathe, states Danny Benjamin, an epidemiologist at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina.
In addition, Ladhani states, since many people have been separated over the previous 18 months– an extremely uncommon scenario– the information that do exist particularly from schools dont show the function that kids and schools would play in a pandemic if people were moving more easily. Numerous schools still have distancing requirements and kids may not be connecting with one another as much in other locations because their households are avoiding social contact.
Still, if childrens body immune systems do combat the infection rapidly, that means they have less virus to spread out. One study of more than 2,500 individuals in Iceland, where the government attempts to track every Covid-19 exposure and infection, appears to bear this out. Researchers discovered that individuals over 16 years of ages were nearly 60 percent more contagious than kids.
Why cant kids under 12 be vaccinated?
Contributing to the difficulty, the experiences from other, recognized vaccines are of little help due to the fact that numerous vaccines are specifically offered in youth, not adulthood, making contrasts hard. And in the case of vaccines that are offered to all age groups, such as the influenza vaccine, grownups have currently had a chance to install an immune action due to the fact that of previous direct exposures. That isnt the case for Covid-19.
To collect more details, the FDA recently asked Pfizer and Moderna to expand the variety of 5- to 11-year-olds in their trials to guarantee that they will discover any rare negative effects. Far, those appear to be very little in 12- to 18-year-olds– the youngest people who can currently receive the vaccine in the United States.
This short article belongs to Reset: The Science of Crisis & & Recovery, an ongoing Knowable Magazine series exploring how the world is browsing the coronavirus pandemic, its effects and the way forward. Reset is supported by a grant from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
” Theres a lot to find out about how kids and adults react differently,” Farber says. “Its a natural experiment, with the whole world all reacting to a brand-new pathogen.” It is heartening though, she says, that children ages 12 to 15 appear to have a slightly more powerful immune action to the mRNA vaccines than adults do.
Knowable Magazine is an independent journalistic endeavor from Annual Reviews.
If the trial works out, Pfizer and Moderna plan to send emergency situation use applications to the FDA that will permit 5- to 11-year-olds to be vaccinated, and the FDA forecasts that the vaccines will be available by midwinter.
There is no proof yet that the delta variation is more hazardous to kids than previous versions of the virus, but vaccines are not yet readily available for kids under 12, numerous places have loosened public health limitations, and delta is so contagious that it is spreading rapidly. That all-time portion has progressively inched up due to an increased percentage of child Covid cases more recently: In the week ending August 26, 2021, kids represented about 22.4 percent of US Covid cases. Tracking a group of adults and kids with Covid-19, it found that the blood of kids and youth under 24 included greater levels of cytokine proteins called IL-17a and IFN-γ, which advise the inherent immune system to attack. Transmission by children has actually been exceptionally difficult to study, not least due to the fact that many children never show symptoms of the virus at all. And though kids do still spread out the virus, its hard to understand how important schools are in that transmission chain.
Regulative firms like the US Food and Drug Administration normally move more very carefully when authorizing treatments for kids. Ethical factors to consider and logistics are more tough when working with kids. Still, its normally expected that they will be safe and reliable in kids.
Data from more than 5 million immunized individuals in Israel showed a small threat of myocarditis– 148 cases– amongst young males who received Pfizers mRNA vaccine. That is mainly why the UK has not yet fully authorized vaccines for kids under 16, Ladhani states.