Its so good that we didnt see cosmic gamma rays until the 1960s when gamma-ray detectors were launched into area to look for signs of atomic weapons tests. Even then, what we observed were extreme flashes of gamma rays known as gamma ray bursts.
Gamma rays strike Earth from all directions of the sky. Our planet is bathed in a diffuse radiance of high-energy photons. It does not affect us much, and we dont truly see it, due to the fact that our atmosphere is excellent at absorbing gamma rays. Its so good that we didnt notice cosmic gamma rays till the 1960s when gamma-ray detectors were launched into space to search for indications of atomic weapons tests. Even then, what we discovered were extreme flashes of gamma rays referred to as gamma ray bursts.
Gamma-ray bursts are brief but brilliant. They are so brilliant that it was first feared they were brought on by nuclear blasts in the world, but we now know they are caused by large passing away stars as their core collapses into a great void. The collapse can set off the development of jets of product streaming away from the star at nearly the speed of light. When the jet hits interstellar gas, it develops a beam of gamma rays. If the jet of a dying star occurs to be pointed in our instructions, we find a gamma-ray burst.
As our gamma-ray telescopes became more sensitive, we likewise spotted a galactic gamma-ray glow. Most of these gamma rays pertain to us from the airplane of the Milky Way and are triggered by high-energy particles that clash with interstellar gas and dust in our galaxy. There are gamma rays that originate from the active galactic nuclei of far-off galaxies. When supermassive black holes take in matter near them, they are created. If you omit gamma rays from all those known sources, there is still a faint, scattered radiance of gamma rays. They pertain to us from all directions, even from regions that appear to be empty space. Weve never had the ability to find out the source of this faint background, but a new paper in Nature appears to have actually fixed this secret.
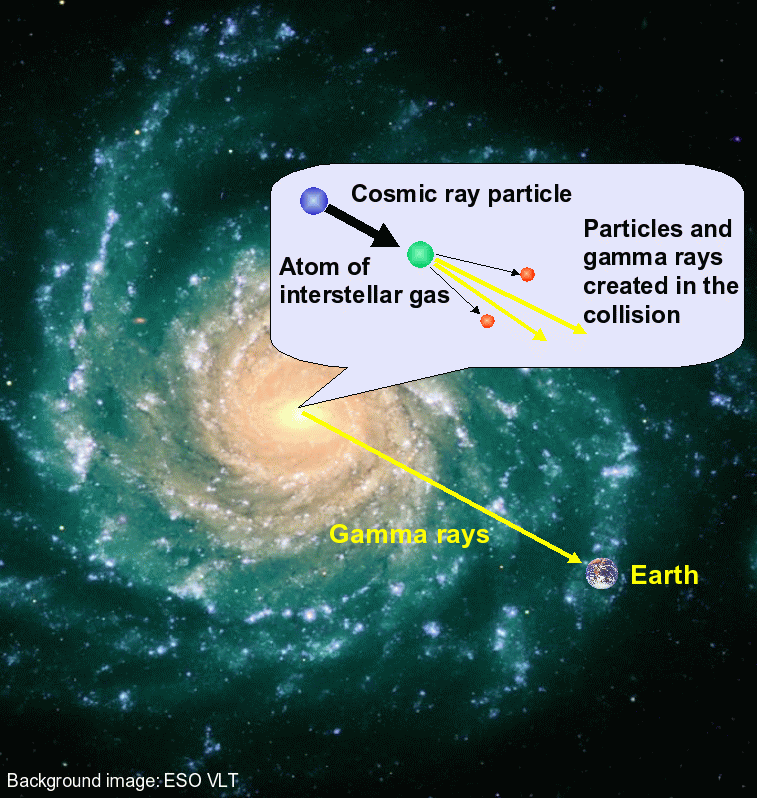
How cosmic ray particles create gamma rays. Credit: Max Planck Intitut/ESO VLT
The team looked at how gamma rays can be produced by cosmic rays. Cosmic rays are incredibly energetic particles, usually protons moving at almost light speed. These cosmic ray particles sometimes strike our environment to produce a cascade of particles we can find on the surface. However cosmic ray accidents can likewise create gamma rays. The team believed the faint gamma-ray background may be caused by cosmic rays striking gas and dust in distant galaxies. Since most of the gas and dust in a galaxy is found in star-forming areas, the group compared the gamma-ray background to the circulation of galaxies actively forming stars. They discovered that star-forming regions in galaxies could be the source of diffuse gamma rays.
When high-resolution gamma-ray telescopes such as the Cherenkov Telescope Array are developed, maps of the gamma-ray background could even more confirm this model. It could also let us study star-forming areas in a new way, and might assist us better understand the origin of cosmic rays.
Referral: Roth, Matt A., et al. “The scattered gamma-ray background is dominated by star-forming galaxies.” Nature 597.7876 (2021 ): 341-344.
Like this: Like Loading …
If you leave out gamma rays from all those recognized sources, there is still a faint, scattered glow of gamma rays. The team looked at how gamma rays can be produced by cosmic rays. Cosmic ray accidents can likewise produce gamma rays.