The strategy uses a phenomenon related to Earths jet stream, called annular modes. Annular modes are variabilities in Earths atmospheric circulation which are not related to seasonal modifications. Battalio wondered if there were comparable weather patterns on locations like Mars and Titan. He and his associates evaluated 15 years of climatic observations from Mars and discovered that, comparable to Earth, the Red Planet has annular modes. Juan Lora, Battalios professor at Yale, also developed a global environment design to browse for annular modes on Titan.
Even meteorologists who forecast the weather condition in the world admit that they cant constantly properly forecast the weather condition at a particular place on our world any provided time. Therefore, trying to anticipate the climatic conditions on another world can be downright impossible.
However a new research study suggests that an oft-used forecasting method on Earth can be used to other worlds too, such as on Mars or Titan, Saturns largest moon.
” I think the very first precise forecasts of possibly a couple of Mars days may be just a decade away,” stated lead author of the study released in Nature Astronomy, J. Michael Battalio, a postdoctoral scientist from Yale University. “It is simply a matter of combining much better observational datasets with sufficiently fine-tuned mathematical models.
The strategy utilizes a phenomenon associated to Earths jet stream, called annular modes. Annular modes are irregularities in Earths climatic circulation which are not associated with seasonal modifications. Annular nodes can impact the jet stream, cloud formation and rainfall throughout the world. These modes likewise describe some of the absence of consistency in wind eddies, or the air circulations in New Englands blizzards and serious Midwest storms.
Battalio wondered if there were comparable weather condition patterns on places like Mars and Titan. He and his associates examined 15 years of climatic observations from Mars and discovered that, similar to Earth, the Red Planet has annular modes. Juan Lora, Battalios professor at Yale, also developed a global environment model to search for annular modes on Titan.
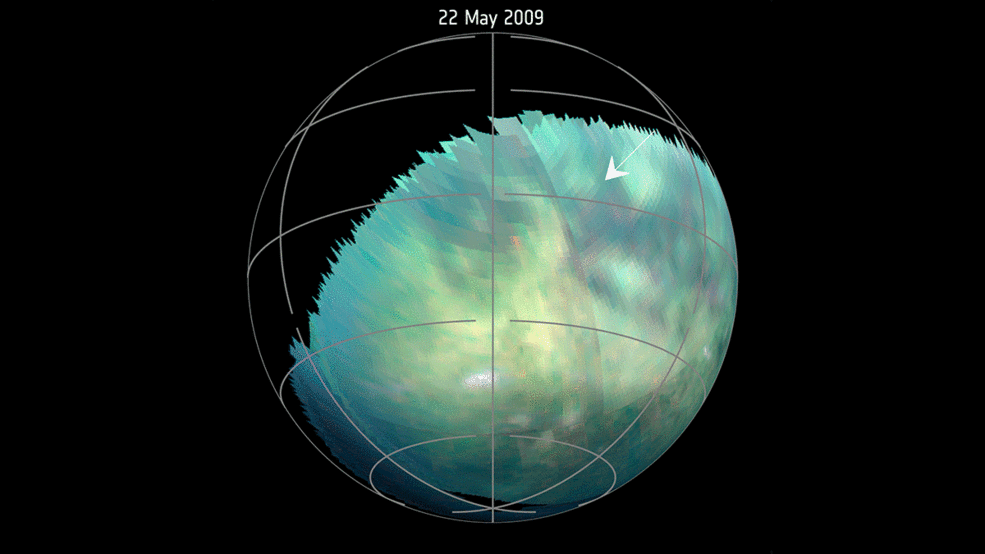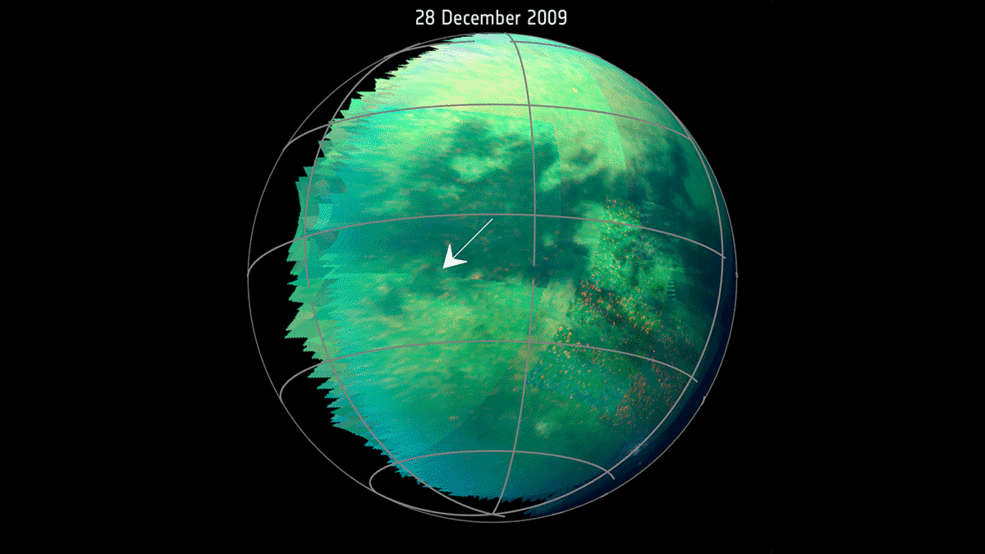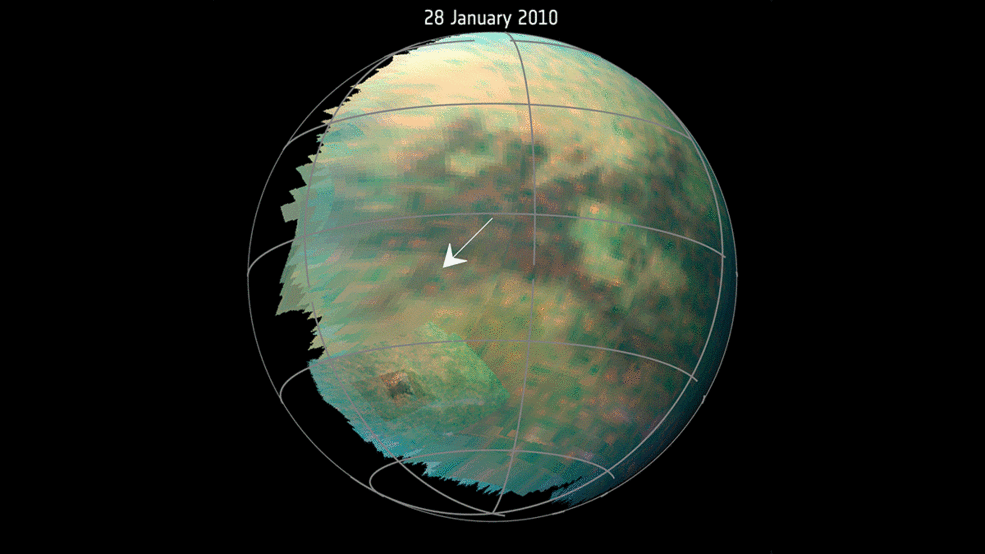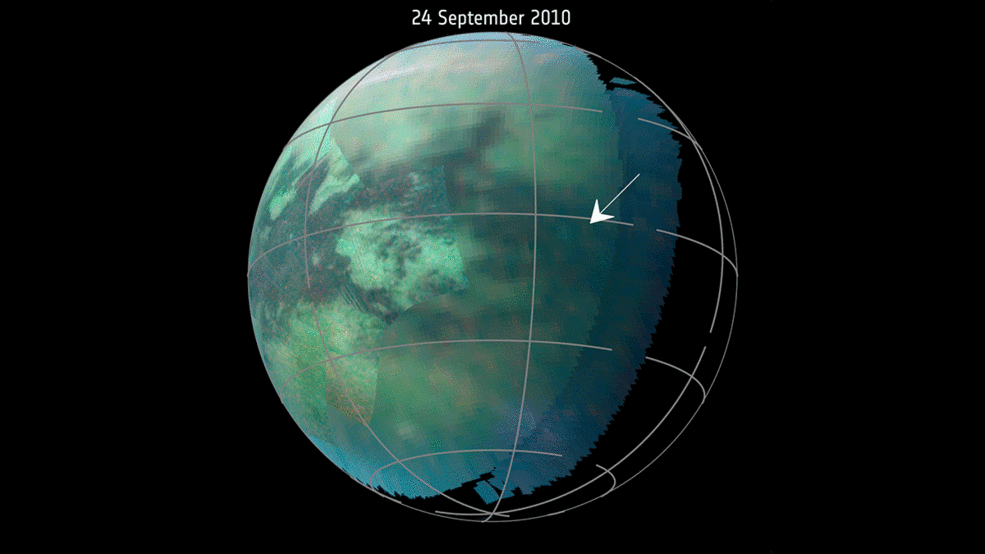
This animation, based on images captured by the Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) on NASAs Cassini objective throughout a number of Titan flybys in 2009 and 2010, reveals clear brilliant spots that have been interpreted as evidence of dust storms. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/University Paris Diderot/IPGP/S. Rodriguez et al. 2018
What they found is that annular modes are most likely much more influential on these 2 worlds than they are on Earth. Annular modes account for half of the wind irregularity on Mars and a minimum of two-thirds of it on Titan.
On Mars, Titan, and Earths modes each occur regularly. Due to the fact that the annular modes affect the eddies that cause dust storms, real-time analysis of the annular modes allows simple forecasts of dust storms without needing to count on a complicated model, the scientists stated.
” The fact that we have actually found annular modes on worlds as different from Earth as Mars and Titan also suggests they might be ubiquitous in planetary atmospheres, from Venus, to the gas giants or exoplanets,” said Battalio, in a press release.
” Methane clouds and surface area modifications triggered by methane rain on Titan have actually been observed in the past,” included Lora. “And now it appears these events are linked to shifts of Titans strong jet stream, affected by its annular modes.”
Weather forecast from Gale Crater on Mars, from the weather condition instrument on the Curiosity rover. Credit: NASA/JPL.
Mars is generally a windy world, with dust storms that can cover the whole planet. Different robotic missions humans have actually sent out to Mars surface have had weather condition instruments, from the Phoenix landers Telltale, which provided wind information, to the Perseverance rovers Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) steps and offers day-to-day and seasonal reports on atmospheric pressure, humidity, ultraviolet radiation at the Martian surface area, air temperature, and ground temperature level around the rover.
The huge selection of images collected by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft have likewise enabled astronomers to get much deeper information on weather condition systems on Mars.
Having the ability to forecast storms on other worlds would be necessary for robotic objectives, but likewise for future human missions as well.
Evidence of dust devils dancing on Mars. Credit: NASA/JPL/UArizona
” Understanding and anticipating these events is vital for the security of objectives, particularly those that count on solar power, however also for all objectives as they arrive on the surface,” Battalio said.
More reading: Yale University Press ReleaseNature Astronomy
Lead image caption: Illustration by Michael S. Helfenbein; Image courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech.
Like this: Like Loading …