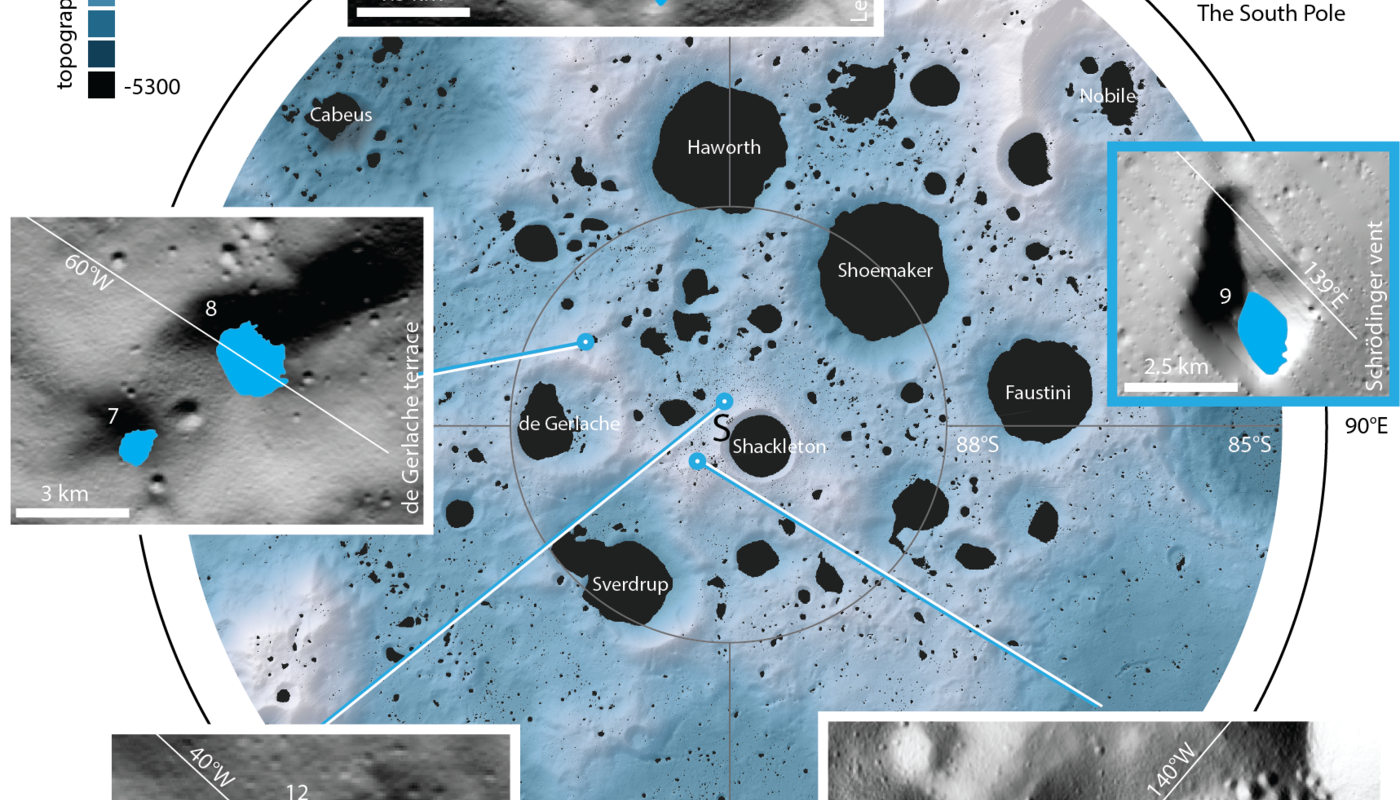
Some of the craters at the lunar south pole that belonged to the study.Credit– MPS/ University of Oxford/ NASA Ames Research Center/ FDL/ SETI Institute.
That is not to state the craters are illuminated at all. Even when they are not in direct sunlight, reflected sunshine, a few of which might have bounced off neighboring hills, is still funnelled into the crater. Any images captured using that reflected light are too “noisy” to make out any in-depth functions..
In addition to removing sound, the software application needs to likewise remedy for other aspects, such as the motion of LRO itself.
Even when they are not in direct sunshine, showed sunlight, some of which may have bounced off nearby hills, is still carried into the crater. In addition to eliminating noise, the software must likewise remedy for other aspects, such as the movement of LRO itself.
These areas have actually captivated researchers for years, in no small part due to the fact that absence of sunshine suggests a lower temperature, permitting frozen materials to stay frozen. So far, no one has been able to image what water is in those craters directly.
These areas have intrigued scientists for years, in no small part since absence of sunlight indicates a lower temperature, permitting frozen materials to stay frozen.
Regrettably, lack of sunlight also indicates its challenging to see whats at the bottom of those craters. The closest scientists have actually come was when LCROSS, a NASA moon objective, fired a projectile into the crater Cabeus and analyzed the resultant dust cloud, which contained a fairly high amount of water. So far, no one has actually been able to image what water is in those craters straight.
UT video going over how we can use water on the Moon.
Regardless of such difficulties, the researchers utilized 70,000 images from LRO to adjust the software, which was then unleashed upon 17 different permanently dark areas at the lunar south pole. The biggest location studied was 54 sq km, while the smallest was a mere 0.18 sq km..
The pictures dont show any direct proof of water, such as intense patches that would suggest ice. Specifying such terrain is where HORUS shines– the scientists might make out geological features a few meters across, which might be possibly hazardous to a lander or rover.
The very same crater with (right) and without (left) information filled out by HORUS.Credit– Left: NASA/LROC/GSFC/ ASU; Right: MPS/University of Oxford/NASA Ames Research Center/FDL/SETI Institute.
This was the primary step toward checking out these formerly invisible parts of the Moon. With luck, someday, people will be able to check out these areas securely, and with much more luck, they might discover a source of a vital ingredient of all Earth-bound life.
Discover more: MPS– Peering into the Moons shadows with AINature– Peering into lunar permanently shadowed areas with deep learningFuntitech– AI supplies an imaging service for the moon shadow craterUT– The Largest Crater on the Moon Reveals Secrets About its Early History.
Lead Image: AI image of the within a crater.Credit– MPS/University of Oxford/NASA Ames Research Center/FDL/SETI Institute.
Like this: Like Loading …
The images dont show any direct proof of water, such as intense spots that would indicate ice.