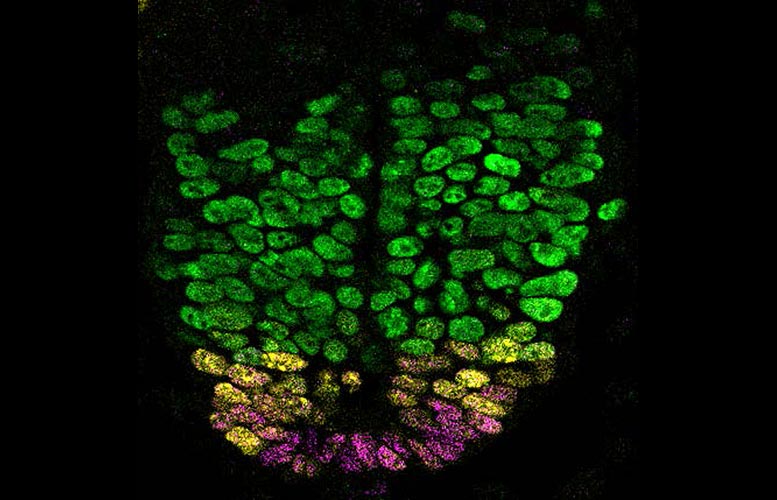
A developing mouse neural tube. Hedgehog signaling is needed to produce various types of neuronal progenitor cells, suggested by the various colors. THC inhibits Hedgehog signaling in genetically susceptible mice, leading to developmental defects, consisting of in the neural tube.
Limited in a lot of nations, the increasing legalization of cannabis for leisure and medical intake implies that cannabis use is rising. Cannabis is likewise the most typical illicit drug utilized by pregnant females, however the results of cannabis on embryonic development are not well understood.
“Several years ago, it was reported that THC could hinder Hedgehog signaling in cells grown in a dish,” stated the studys lead author Robert Krauss, PhD, Professor of Cell, Developmental and Regenerative Biology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “We reasoned that THC might be an ecological danger aspect for birth defects, however that it would need extra danger factors, such as specific anomalies in the genes required for Hedgehog signaling, to induce these flaws in mice.”.
To resolve this hypothesis, Dr. Krauss and associates administered a single dose of THC, equivalent to direct exposures achieved when humans smoke marijuana, to pregnant mice about a week after conception. They then studied the embryonic advancement of their pups, a few of which carried a mutation that suggested Hedgehog signaling was not working at complete efficiency. The scientists found that pups without the mutation developed usually, even when exposed to THC, as did pups that carried the anomaly but were not exposed to the drug. However, puppies that were exposed to THC and carried the anomaly developed a brain and face problem called holoprosencephaly, a typical birth problem seen in 1 in 250 human conceptions that consists of the failure of the forebrain to divide into two distinct sectors.
THC inhibits Hedgehog signaling in genetically prone mice, leading to developmental problems, including in the neural tube. “We reasoned that THC might be an environmental danger factor for birth defects, however that it would need extra risk factors, such as particular anomalies in the genes required for Hedgehog signaling, to cause these problems in mice.”.
The scientists showed that the defect occurs due to the fact that THC can interfere with Hedgehog signaling in the embryo. THC alone is not enough to disrupt Hedgehog signaling and cause problems but, in animals where Hedgehog signaling is already weakened through hereditary anomaly, it has substantial effects. “THC directly prevents Hedgehog signaling in mice, however it is not a very effective inhibitor; this is probably why a hereditary predisposition is needed for it to cause holoprosencephaly in mice,” discussed Dr. Krauss.
The scientists showed that the flaw occurs since THC can hinder Hedgehog signaling in the embryo. THC alone is not enough to interrupt Hedgehog signaling and trigger flaws however, in animals where Hedgehog signaling is already damaged through genetic mutation, it has substantial impacts. “THC straight prevents Hedgehog signaling in mice, however it is not an extremely effective inhibitor; this is most likely why a hereditary predisposition is required for it to trigger holoprosencephaly in mice,” described Dr. Krauss.
These first studies in mice have important ramifications for human health, highlighting the need for more research into the effects of cannabis usage during pregnancy in people. “The THC concentration in marijuana is now extremely high, so it is essential to carry out public health studies looking at whether cannabis intake is associated with developmental flaws.
This research study focussed on one chemical in cannabis and one genetic mutation, further research might expose other mixes that cause similar effects. “Many of the mutations found in human holoprosencephaly patients might conceivably synergize with THC,” stated Dr. Krauss. “We would likewise like to test the associated chemical CBD in genetically predisposed mice. Like THC, CBD inhibits Hedgehog signaling in cells grown in a meal, but CBD appears to work differently. As CBD is extensively offered and often deemed beneficial– or at least innocuous– it would be worth investigating this too,” he included.
Referral: “Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol prevents Hedgehog-dependent patterning during advancement” 5 October 2021, Development.DOI: 10.1242/ dev.199585.