Earth ultimately partly cleaned out its orbital path, culminating in the period called the Late Heavy Bombardment.
What was the Late Heavy Bombardment that pummelled Earth for millions of years?Credit– History of the Earth YouTube Channel.
It turns out they werent– present barrage designs led to about 10 times less spherule layers that have been discovered in the geological record. Subsequently, that indicates up to 10 times more major asteroid effects in that period than models had anticipated.
That much more impacts might have had a substantial effect on among the most crucial ecological factors of the early Earth– its oxygen level. After discovering the discrepancy in between the model predictions and the geological data, scientists proceeded to modeling what influence these impacts would have on the worlds ecological chemistry.
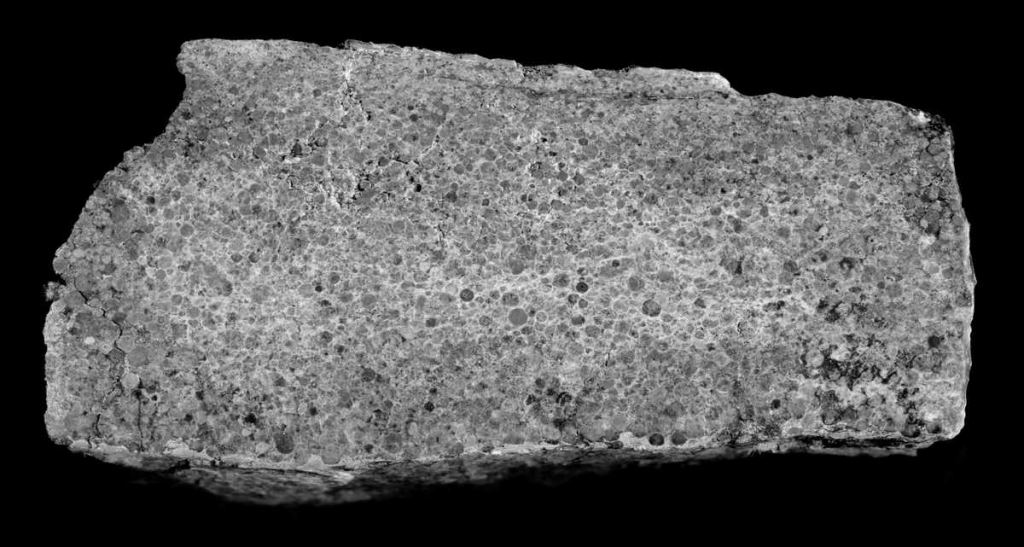
Cross-section of a spherule layer produced by a significant asteroid impact.Credit– SwRI.
Unsurprisingly, it had a pretty significant effect. Big effects, such as those producing spherule layers, can produce reactive gases that react with oxygen to pull it out of the atmosphere. According to the geological record, for much of Earths early history, it had extraordinarily low oxygen levels. It turns out that multiple big impactors may have preserved low levels for billions of years.. Those billions of years ultimately ended with what is now understood as the Great Oxidation Event, where climatic oxygen levels spiked dramatically. At that point, Earth had actually cleared out many of the bigger asteroids in its area, so the additional oxygen released into the environment by its burgeoning biosphere wasnt erased by the reactive gases from asteroid impacts..
That event was one of the substantial remarkable shifts in the history of life in the world. Comprehending it now, from up until now in the future, is hard. However it is practical to know that it was partially allowed by Earth cleaning out its orbital course and subjecting itself to considerable penalty for billions of years. Just another example of how many things needed to go right for intelligent life to develop.
Discover more: SwRI– SwRI-LED TEAM PRODUCES A NEW EARTH BOMBARDMENT MODELJPost– Ancient asteroids struck Earth regularly, delayed increase of life– studyUT– Leftover Material Caused the Late Heavy BombardmentUT– Evidence of a Late Heavy Bombardment Occuring in Another Solar System.
Lead Image: Artists depiction of asteroids impacting the early Earth.Credit– SwRI.
Like this: Like Loading …
Early on, the planetary system was much more populated with space rocks. Those space rocks were known to strike Earth, and speculation is plentiful about what took place when they did so. Earth ultimately partly cleaned up out its orbital course, culminating in the period called the Late Heavy Bombardment.
Understanding it now, from so far in the future, is challenging. Simply another example of how so lots of things had to go right for smart life to progress.
Not as numerous rocks hit the Earth in its later years, but the ones that did had a substantial impact.
While the damaging power of that time period has been well documented, big asteroids continued to affect the Earth consistently for billions of years. When they did so, they formed “impact spherules” of molten rock that were thrown into the air, strengthened, and then landed back on the Earths surface area. They became distinct sand-grain-sized round elements of the geological layers set when their effect occurred..
There are multiple spherule layers in the geologic record, showing that impacts large enough to develop sky-bound ejecta prevailed. More have actually been discovered recently, leading scientists to analyze whether the newly found abundance of these spherule layers was accounted for in simulations of early asteroid barrage.
Price quotes vary on how much product affected the world, however it had a considerable result on the planets atmosphere and the development of life. That much of a distinction might significantly alter how geologists and planetary researchers view the early Earth.
Quotes vary on how much product impacted the world, however it had a substantial result on the planets environment and the development of life. That much of a distinction could significantly change how geologists and planetary scientists view the early Earth.