Researchers utilizing the Alice UV imaging spectrograph on board New Horizons, have been patiently however sporadically gathering data throughout those 15 years, however likewise waiting to get far enough away from the Sun to make a particular measurement: the brightness of the Lyman-alpha background of the Milky Way.” The further we moved away from the Sun, the less we were blinded by the solar part of the Lyman-alpha background,” said New Horizons group member Dr. Randy Gladstone, author of a brand-new paper released in the Astronomical Journal. The Alice UV imaging spectrograph has been used to study the structure of environment and search for atmosphere around Charon, as well as step the Lyman-alpha ultraviolet background in our galaxy. Lead image caption: This false-color map reveals several scans of the Lyman-alpha background over the sky, obtained by the Alice ultraviolet spectrograph on the New Horizons spacecraft when it was 45 AU from the Sun. The information agrees well with an underlying design of the solar part of the Lyman-alpha background to which a constant brightness from the Milky Way has been added.
The New Horizons spacecraft has been speeding away from Earth because it introduced in 2006. Researchers utilizing the Alice UV imaging spectrograph on board New Horizons, have actually been patiently but sporadically collecting information throughout those 15 years, but likewise waiting to get far enough far from the Sun to make a particular measurement: the brightness of the Lyman-alpha background of the Milky Way. Until now, this had actually never been measured properly.
” The farther we moved far from the Sun, the less we were blinded by the solar part of the Lyman-alpha background,” said New Horizons team member Dr. Randy Gladstone, author of a new paper released in the Astronomical Journal. “This has been something thats been rated by astronomers for years. Now we have a much more exact number.”
Gladstone and his team utilized Alice to make the observations of the Lyman-alpha background (Ly?) numerous times during the objective: Three times during the cruise to Pluto, another observation simply one month prior to the objectives flyby of Pluto, in addition to one day after, and 5 times ever since, out to simply over 47 au from the Sun.
What Alice found is that the stellar element of the Lyman-alpha background has to do with 20 times less bright than the Lyman-alpha background is near Earth.
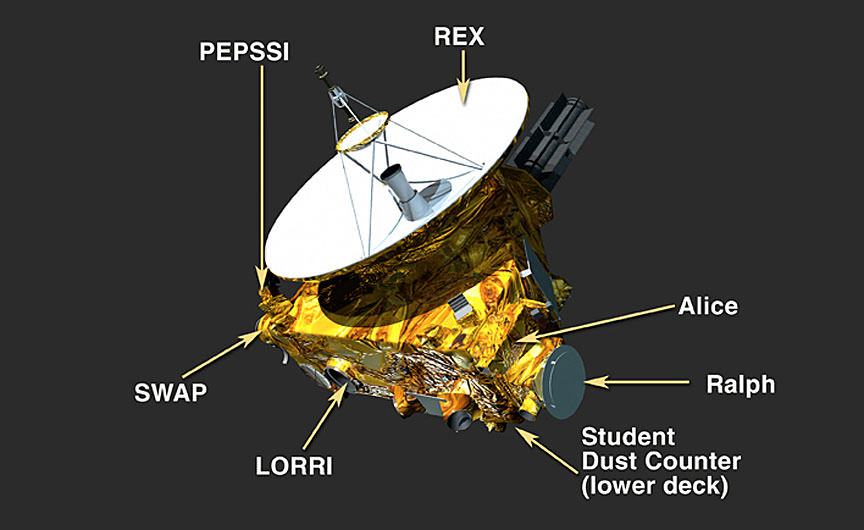
Instruments on New Horizons. The Alice UV imaging spectrograph has actually been utilized to study the structure of environment and look for atmosphere around Charon, in addition to measure the Lyman-alpha ultraviolet background in our galaxy. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute.
The Lyman-alpha ultraviolet background was first detected in the 1960s, and previously, researchers have actually just been able to makes estimates of how pervasive it is– and these price quotes have varied widely over the last 60 years.
The Lyman-alpha ultraviolet background radiance permeates area and can be used to identify the rare wind of hydrogen atoms which blows through our Solar System. Studying this wavelength of light– which is about four times much shorter than what human eyes can see– permits astronomers to actually see in the dark. Observational cosmologists have had the ability to map out the circulation of matter in deep space, and an instrument similar to Alice on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter called LAMP (Lyman Alpha Mapping Project) was utilized to image completely dark craters near the north and south poles of the Moon.
A map showing the completely watched areas (blue) that cover about 3 percent of the moons south pole. Credit: NASA Goddard/LRO objective.
In area, the galactic Lyman-alpha background comes from hot areas around massive stars which ionize all the matter near them, which is mostly hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms in between the stars scatter these photons into a roughly uniform glow throughout space. But in the majority of our solar system, the background is dominated by Lyman-alpha photons discharged by the sun.
” The Lyman-alpha background has been studied a lot near the Earths orbit, and is intense enough that if we might see it, the night sky would never ever get darker than twilight,” Gladstone explained in a press release. “Its so bright from solar Lyman-alpha that we werent particular how much the Milky Way galaxy contributed to its general brightness.
Out in the Kuiper Belt where New Horizons is traveling, the spread sunlight component of the Lyman-alpha signal is far less bright and the fainter components from the close-by regions of the Milky Way end up being easier to identify. The group said in their paper that a more exact measurement will assist astronomers much better understand the neighboring areas of the Milky Way galaxy.
” What an excellent resource New Horizons is,” stated New Horizons principal detective Alan Stern, “not simply for the exploration of the Kuiper Belt, but also to comprehend more about our galaxy and even deep space beyond our galaxy through this and other observations by our clinical instrument payload.”.
Lead image caption: This false-color map shows a number of scans of the Lyman-alpha background over the sky, obtained by the Alice ultraviolet spectrograph on the New Horizons spacecraft when it was 45 AU from the Sun. The data agrees well with an underlying design of the solar element of the Lyman-alpha background to which a consistent brightness from the Milky Way has been added.
Like this: Like Loading …