The vaccines still work, and for most individuals, still supply a high level of protection versus serious disease. Development infections have actually increased but infections are still three times more likely in unvaccinated than immunized individuals. Of those infections, only 3.9 percent have actually led to hospitalization in vaccinated clients compared to 9 percent in those who stay unvaccinated.
To find out more about waning immunity and how to safeguard against it, we connected to the specialists.
New variants likewise contribute in subsiding immunity. Mutations like those seen in the brand-new Omicron variant may assist the virus slip past our body immune system, however researchers dont yet know if this holds true for Omicron.
When Pfizer, Moderna and Johnson & & Johnson announced their Phase 3 clinical trial results, suggesting that their injections were 95 percent, 95 percent and 67 percent efficient at avoiding infection, respectively, specialists cheered. All 3 vaccines supplied what seemed to be nearly impenetrable walls against extreme COVID-19 illness. As the pandemic has actually worn on and reports of advancement infections made national headlines, the FDA and CDC advised a shot to increase immunity among all grownups 6 to eight months after their 2nd shot of Pfizer or Modernas vaccine, or two months after the very first shot of Johnson & & Johnson
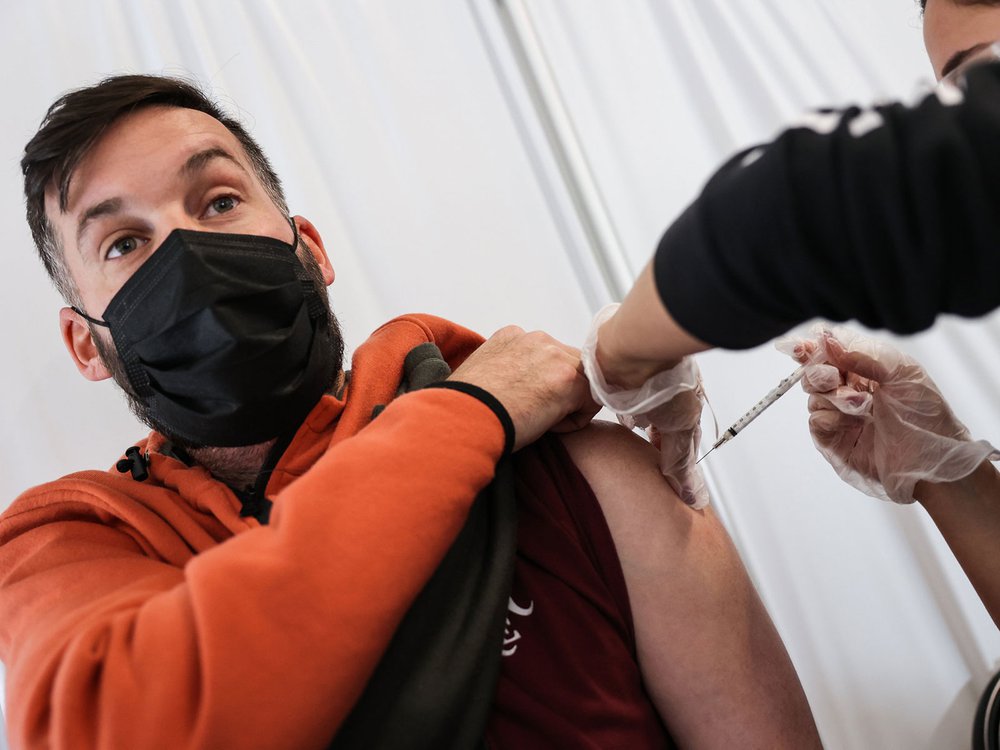
A booster shot is administered in Stony Brook, New York in November. Such a shot can help spur a persons body immune system to ramp up defenses versus Covid-19.
Steve Pfost/ Newsday RM by means of Getty Images
. Anthony Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases recently told the New York Times that immunity is “subsiding to the point where youre seeing a growing number of individuals getting development infections, and more and more of those individuals who are getting breakthrough infections are ending up in the health center … boosters will be a crucial part of the security.”
1. What occurs when you get the COVID-19 vaccine?
Weve been hearing about antibodies considering that the beginning of the pandemic, and for excellent reason. These proteins are among the most important components of immunity and theyve also been utilized in both screening and treatment for COVID-19. Theyre created by B cells.
Vaccination stimulates B cells to produce the SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies that fill your blood after infection or vaccination and attach to various parts of the virus. Neutralizing antibodies are your best defense. They hold on to the spike protein on the outside of the virus which stops it from entering your cells, effectively reducing the effects of the risk.
Vaccination likewise stimulates the production of T cells. Instead of recognizing the virus alone, like an antibody, T cells find and eliminate your own cells after theyve been infected, so the infection cant spread. “The T cells are not that great in preventing an infection however definitely vital for terminating an infection,” states Alessandro Sette, an infectious illness and vaccine researcher at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology. “If you have a good T cell action, youll have less extreme illness.”
Your body immune system has 3 main soldiers that work together to acknowledge and stop infections from ruining your body: antibodies, B cells and T cells.
” Antibodies are wonderful. They look after a great deal of infections that are floating around in your body,” states Kennedy. “But when the virus enters a cell, antibodies cant do anything about it. So thats where your T cells come in.”
2. What does waning immunity appear like?
After your antibody levels fall, a small percentage of B and T cells will stick around as “memory cells,” which can live for months, years and often even years. If the virus (or a booster shot) returns, these cells can quickly ramp up your immune action. If they dont see the infection again, even they ultimately begin to pass away and your resistance will subside further.
Your B cells keep producing– and even enhancing– antibodies particular to the virus for some time. “Imagine the B cells and the T cells as soldiers that are there battling an infection and antibodies are bullets that are shot by B cells,” states Sette.
How long the cells stick around depends on what virus theyre trained to kill. While SARS-CoV-2 antibodies start to wane after a couple of months, scientists do not yet know how long memory B and T cells stick around.
3. What does subsiding immunity look like with COVID-19 vaccines?
If you have a very high level of antibodies, theyll wipe out the virus before an infection can take hold and you will not experience any symptoms. If your antibodies subside a little, it may take a bit longer for your immune system to wipe the virus out, but the disease will be moderate and relatively brief.
” Initially, we saw antibodies declining, but defense was [still] high,” says Slifka. Now, “security versus extreme illness is likewise waning, however not as rapidly.”.
About six to eight months after your 2nd jab of Pfizer or Moderna or two months after your very first of Johnson & & Johnson, your antibody levels start to fall, and researchers have actually found your probability of getting a breakthrough infection increases, though youre still primarily safeguarded from extreme disease and death. This is the start of subsiding resistance.
” Were seeing a lot of breakthrough cases,” states Rosemary Rochford, an immunologist at the University of Colorado, Anschultz School of Medicine. “But we dont see as much advancement disease.” Those with advancement infections are still far less likely to wind up in the health center than those who are unvaccinated.
4. Can an antibody test tell me if I need a booster shot?
Not. There are two primary reasons for this. Initially, scientists havent determined the specific level of antibodies you require to be safeguarded, called an immune correlate of protection. To do this, they d need to have access to blood samples taken from an immunized population practically immediately before a break out. They can examine the number of antibodies in each blood sample and compare that to who got sick and how sick, while presuming that their direct exposure to disease was about the same.
The other reason researchers dont know when each individual requirements booster shots is that antibody levels only inform part of the story. “If you have a lot of antibodies, you dont need any of those other immune functions. That implies that even if you had a really low level of antibodies, you could still be safeguarded.
Its taken some serendipity to discover this limit for some other illness. Using samples from the contributed blood, researchers might compare the level of antibodies leftover from vaccination in each sample with who got sick and who didnt and discover the level at which individuals lost defense.
5. What function do new versions play?
T cells formed after infection or vaccination install robust immune actions against the Delta variation, according to a September 2021 correspondence in Nature. The authors of the forecast that patients whose antibodies do not reduce the effects of the Delta variation will experience mild advancement infections, but “if the T cells are still there, its likely that they will still have the ability to avoid serious disease,” says Sette.
Scientists are running experiments now to see how the vaccines fare versus Omicron. Its not yet understood whether the mutations in its spike protein assist it evade immunity, or impact the transmission or severity of illness.
Nevertheless, the Delta version is far more transmittable than previous variants, suggesting that an individual with this strain usually carries far more viruses than someone infected with another pressure. Instead of concealing from the immune system, sometimes it can overwhelm it with huge numbers. “If you have one virus get in a body with 100 antibodies, breeze, you can cover it up and you will not get infected.” Says Rochford. “Now, if you have 1000 infections get in and youve got 100 antibodies, you can overwhelm [the antibodies] and it takes a little bit longer [for the antibodies to overcome the infection] so you can establish that infection.”.
As the virus mutates, its possible that the modifications permit it to evade our immune systems recognition. This is why theres a new influenza vaccine every year– the virus alters so quickly that the previous years shot does not offer appropriate security the next year.
Because a booster shot can increase your level of antibodies, it can assist protect against the Delta variant. In addition, when scientists took blood samples from individuals after their very first and 2nd doses of the Pfizer vaccines, they discovered that after the second shot, antibodies had the ability to neutralize more strains of the virus. “The booster dosage not just increases the magnitude of the antibody response, however also increases the breadth to various variations that arent even in the solution,” states Slifka.
A number of brand-new versions of SARS-CoV-2 have emerged– and some, like Delta and Omicron, have anomalies in the spike protein that may help them avoid antibody detection– however none have been entirely able to elude vaccine-induced immunity.
6. So when should I get my 3rd shot?
To Rochford, the response to when to get a booster is simpler. “When you can,” she states.
Kennedy adds that in addition to the rate at which your resistance subsides, you should consider your danger of direct exposure. Ask yourself what youll be doing over the next few months. You might consider getting your booster shot quicker rather than later if your plans include traveling or large gatherings like sporting events and household get-togethers.
Vaccines.
COVID-19.
Disease and Illnesses.
Health.
Everyones immunity subsides at different rates, so the CDC and FDA have had to determine the time that appears to make the most sense for a lot of people. “You do not want to inform everyone you have to get a booster on a monthly basis. That would absolutely supply a great deal of protection today youre over-vaccinating individuals,” says Kennedy. Breakthrough infections appear to end up being more common around six to eight months after two doses of Pfizer or Moderna, which is why thats the suggested timeline. If you have a compromised immune system, you must consider getting a third shoot earlier, suggests Kennedy, however for most individuals, anywhere in the six-to-eight-month variety would be practical for those with the mRNA vaccines. Regulators recommend a 2nd shot 2 months after getting the very first Johnson and Johnson vaccine.
Advised Videos.
Vaccination spurs B cells to churn out the SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies that fill your blood after infection or vaccination and attach to different parts of the infection. “But as soon as the infection gets inside a cell, antibodies cant do anything about it. Rather of recognizing the virus alone, like an antibody, T cells find and eliminate your own cells after theyve been infected, so the virus cant spread. “Imagine the B cells and the T cells as soldiers that are there fighting an infection and antibodies are bullets that are shot by B cells,” states Sette. After your antibody levels fall, a small percentage of B and T cells will stick around as “memory cells,” which can live for months, years and in some cases even decades.
Medication.
Disease.