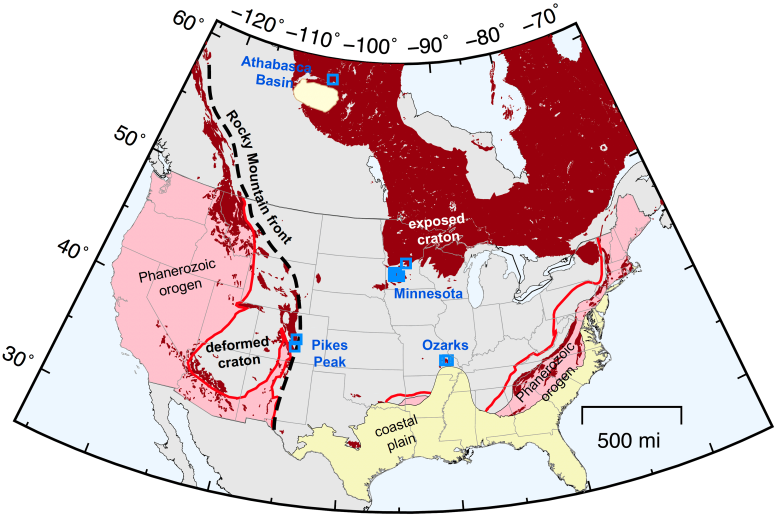
The enormous quantity of missing rock that has actually happened referred to as the Great Unconformity was initially named in the Grand Canyon in the late 1800s. The obvious geological function shows up where rock layers from remote period are sandwiched together, and it is typically recognized where rocks with fossils sit straight above those that do not consist of fossils.
In Colorados Ladder Canyon, rocks that vary in age by about a billion years sit together throughout the Great Unconformity. Credit: C. Brenhin Keller
” This was a remarkable time in Earths history,” stated Kalin McDannell, a postdoctoral scientist at Dartmouth and the lead author of the paper. “The Great Unconformity sets the phase for the Cambrian surge of life, which has actually constantly been perplexing considering that it is so abrupt in the fossil record– evolutionary and geological processes are typically steady.”
For over a century, researchers have looked for to discuss the cause of the missing geological time.
In the last 5 years, two opposing theories have actually entered into focus: One explains that the rock was carved away by ancient glaciers during the Snowball Earth period about 700 to 635 million years ago. The other concentrates on a series of plate tectonic occasions over a lot longer duration during the assembly and separation of the supercontinent Rodinia from about 1 billion to 550 million years ago.
Research led by Keller in 2019 first proposed that widespread disintegration by continental ice sheets throughout the Cryogenian glacial interval triggered the loss of rock. This was based upon geochemical proxies that recommended that big amounts of mass erosion matched with the Snowball Earth period.
” The brand-new research confirms and advances the findings in the earlier research study,” stated Keller. “Here we are supplying independent evidence of rock cooling and miles of exhumation in the Cryogenian period throughout a big location of North America.”
The research study counts on a comprehensive analysis of thermochronology to make the evaluation.
C. Brenhin Keller, assistant teacher of earth sciences, left, and Kalin McDannell, a postdoctoral scientist in earth sciences. Credit: Eli Burakian/Dartmouth College
Thermochronology allows researchers to estimate the temperature that mineral crystals experience in time along with their position in the continental crust given a specific thermal structure. When missing out on rock was eliminated and when rocks presently exposed at the surface area might have been exhumed, those histories can offer proof of.
The scientists utilized multiple measurements from previously published thermochronometric information taken across 4 North American locations. The locations, understood as cratons, belong to the continent that are chemically and physically steady, and where plate tectonic activity would not have actually prevailed during that time.
By running simulations that looked for the time-temperature path the rocks experienced, the research taped an extensive signal of fast, high magnitude cooling that follows about 2-3 miles of erosion during Snowball Earth glaciations throughout the interior of North America.
” While other research studies have actually used thermochronology to question the glacial origin, an international phenomenon like the Great Unconformity requires a global assessment,” stated McDannell. “Glaciation is the most basic description for erosion throughout a vast area during the Snowball Earth duration considering that ice sheets were believed to cover many of North America at that time and can be effective excavators of rock.”
According to the research study team, the contending theory that tectonic activity carved out the missing out on rock was put forth in 2020 when a different research study group questioned whether ancient glaciers were erosive enough to trigger the massive loss of rock. While that research study also utilized thermochronology, it used an alternate method at only a single tectonically active area and recommended that the erosion took place prior to Snowball Earth.
” The underlying idea is quite easy: Something eliminated a great deal of rock, leading to a great deal of missing out on time,” stated Keller. “Our research demonstrates that only glacial disintegration could be accountable at this scale.”
According to the researchers, the brand-new findings also help describe links between the erosion of rock and the development of complex organisms about 530 million years ago throughout the Cambrian surge. It is believed that disintegration during the Snowball Earth duration deposited nutrient-rich sediment in the ocean that could have provided a fertile environment for the foundation of intricate life.
The study keeps in mind that the 2 hypotheses of how the rock worn down are not equally special– it is possible that both tectonics and glaciation added to international Earth system interruption throughout the development of the Great Unconformity. It appears, nevertheless, that only glaciation can discuss disintegration in the center of the continent, far from the tectonic margins.
” Ultimately with regard to the Great Unconformity, it might be that the usually accepted restoration( s) of more concentrated equatorial packing of the Rodinian continents in addition to the special environmental conditions of the Neoproterozoic, proved to be a time of geologic serendipity unlike many any other in Earth history,” the term paper says.
According to the team, this is the very first research that uses their thermochronology modeling method to study a duration that extends well beyond a billion years. In the future, the group will duplicate their deal with other continents, where they hope to more test these hypotheses about how the Great Unconformity was produced and protected.
According to the team, dealing with distinctions in the research is critical to understanding early Earth history and the affiliation of weather, biogeochemical and tectonic procedures.
” The reality that there may have been tectonic erosion along the craton margins does not rule out glaciation,” said McDannell. “Unconformities are composite functions, and our work recommends Cryogenian erosion was a crucial contributor, but it is possible that both earlier and later on disintegration were associated with forming the unconformity surface area in various places. A global evaluation will tell us more.”
Recommendation: “Thermochronologic constraints on the origin of the Great Unconformity” 25 January 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.DOI: 10.1073/ pnas.2118682119.
William Guenthner, from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; Peter Zeitler from Lehigh University; and David Shuster from the University of California, Berkeley and the Berkeley Geochronology Center functioned as co-authors of the paper.
Scientists used thermochronometric data from 4 North American areas to identify the reason for the “Great Unconformity”– a huge loss of rock about 700 million years ago. Credit: Figure by Kalin McDannell
Ice action seems accountable for ancient disintegration of rock throughout the planet.
New research study provides more proof that rocks representing approximately a billion years of geological time were sculpted away by ancient glaciers during the planets “Snowball Earth” period, according to a research study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research study provides the most current findings in a dispute over what triggered the Earths “Great Unconformity”– a time space in the geological record connected with the erosion of rock approximately 3 miles thick in areas across the world.
” The truth that a lot of places are missing out on the sedimentary rocks from this time period has been one of the most puzzling functions of the rock record,” said C. Brenhin Keller, an assistant teacher of earth sciences and senior researcher on the research study. “With these outcomes, the pattern is starting to make a lot more sense.”