What if our eyes could see radio waves?
We may be able to look up into the sky and see a tunnel of rope-like filaments made of radio waves if we could. The structure would be about 1,000 light-years long and would be about 350 light-years away.
This tunnel explains 2 of the brightest radio features in the sky.
Astronomers discovered the North Polar Spur and the Fan Region in the 1960s when radio astronomy was getting going. It produces x-rays and radio waves.
The Fan Region is one of the most dominant polarized radio functions in the sky. Theres debate about the nature of the Fan Region, too, with some saying its a local function and some arguing that its on a galactic scale.
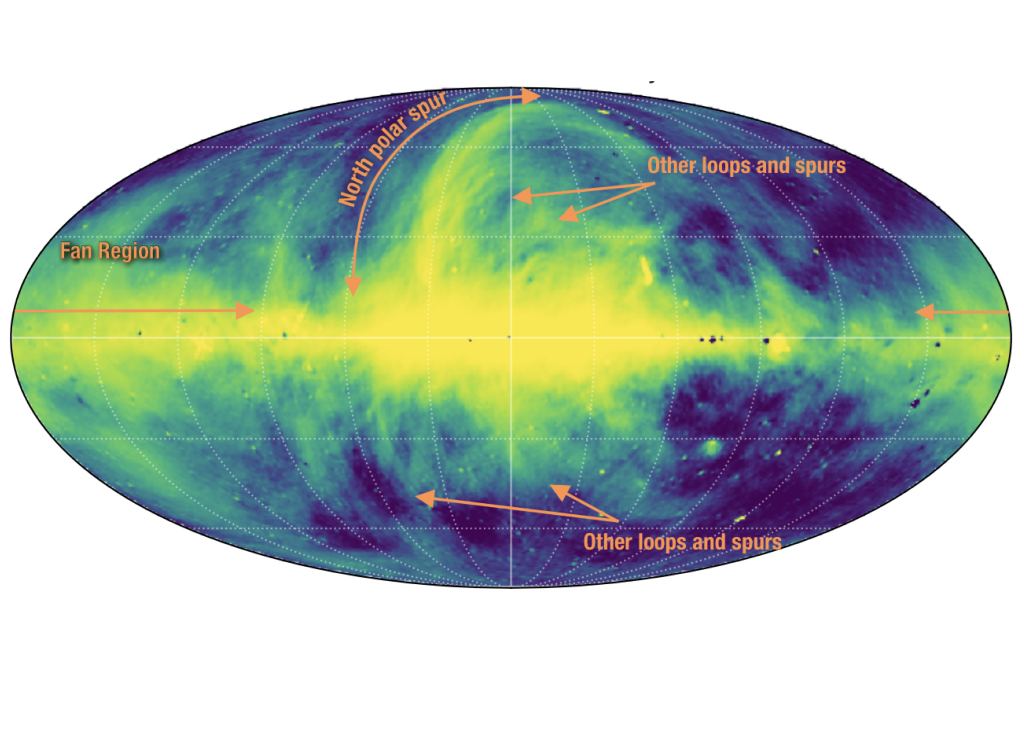
The Galaxy is seen in radio waves in the standard view with the Galactic centre in the middle of the image. Credit: Haslam et al. (1982) with annotations by J. West.
A team of researchers from Canada and the United States presents proof in a brand-new paper revealing that the pair of features are linked. The papers title is “A Unified Model for the Fan Region and the North Polar Spur: A bundle of filaments in the Local Galaxy.” The lead author is Dr. Jennifer West, Research Associate at the Dunlap Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Toronto.
” If we were to look up in the sky, we would see this tunnel-like structure in simply about every direction we looked– that is, if we had eyes that could see radio light.” Dr. Jennifer West, Dunlap Institute for Astronomy
The authors state that both the NPS and the Fan Region become part of the exact same feature. The feature is comprised of 1,000 light-years long “ropes,” which themselves are comprised of charged particles and a magnetic field. Theyre ideal in front of our eyes, but we cant see them. “If we were to look up in the sky,” discusses West, “we would see this tunnel-like structure in just about every instructions we looked– that is, if we had eyes that could see radio light.”
This image from the study shows the tunnel at 30 GHz. The North Polar Spur sweeps up and to the right, while the Fan Region is on the left. Image Credit: West et al., 2021.
” Magnetic fields do not exist in isolation,” West explains in a press release. The technique was to find out how these 2 were linked. West thinks that her team is the first group of astronomers to sign up with the pair of features.
West says shes been believing about the set of features for 15 years given that she first saw a radio map of the sky. In current years shes constructed a computer design that reveals what the radio sky would look like from Earth as she changed the shape and location of the long radio ropes.
A paper from 1965 played a function in the discovery.
” A couple of years earlier, one of our co-authors, Tom Landecker, informed me about a paper from 1965, from the early days of radio astronomy,” West stated. “Based on the unrefined data available at this time, the authors (Mathewson & & Milne), speculated that these polarized radio signals could occur from our view of the Local Arm of the Galaxy, from inside it. That paper inspired me to establish this concept and tie my model to the vastly better data that our telescopes provide us today.”
” Most astronomers take a look at a map with the North pole of the Galaxy up and the Galactic centre in the middle.” Dr. Jennifer West, Dunlap Institute for Astronomy
West compares their deal with a map of the Earth. The North Pole is on top, of course, and the equator remains in the middle. It can be drawn from a various viewpoint, which is what Wests computer design allowed her to do. “Most astronomers take a look at a map with the North pole of the Galaxy up and the Galactic centre in the middle,” she explains. “A fundamental part that motivated this idea was to remake that map with a different point in the middle.”
Left: The sky as it would appear in radio polarized waves. The Van-Gogh-like lines reveal the orientation of the electromagnetic field. These radio data are shown projected as they would be seen in the sky together with the brightest stars and constellations describes and constellation names overlaid. Credit: Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory/Villa Elisa telescope/ESA/Planck Collaboration/Stellarium/J. West. : the sky in the very same orientation and projection, as it can be seen with our eyes. The same brightest stars and constellations as in the previous image are shown. Credit: Stellarium/J. West.
” This is extremely clever work.” Dr. Bryan Gaensler, research study co-author.
” This is very smart work,” states Dr. Bryan Gaensler, a teacher at the Dunlap Institute and an author on the publication. Now Im thrilled to see how the rest of the astronomy neighborhood responds.”
West is a professional in galaxies and the ISM. Shes anticipating more research that can hopefully discover how the different magnetic structures in the sky are connected.
” Magnetic fields dont exist in seclusion,” she discusses. “They all must link to each other. So a next action is to better understand how this local magnetic field connects both to the larger-scale Galactic magnetic field and also to the smaller scale electromagnetic fields of our Sun and Earth.”
This figure from the research study reveals the plan of some of the loops built on nested cylinders. The diagram is not to scale, but the positioning of the filaments is correct with regard to the Suns position and relative to each other. Image Credit: West et al. 2021.
We cant see these structures with our eyes. Knowing theyre out there is thought-expanding.
” I think its simply remarkable to envision that these structures are all over whenever we search for into the night sky,” stated West.
For several years, astronomers have actually argued over the nature of the North Polar Spur. Various research study has actually produced contradictions. Some research studies reveal its a far-off function, while others reveal its more local. West and her co-authors say their paper has solved these contradictions. “We show this model follows the a great deal of observational studies on these areas and is able to deal with an apparent contradiction in the literature that recommends the high latitude portion of the NPS is nearby, while lower latitude portions are more remote.”
” This model has implications for establishing a holistic design of magnetic fields in galaxies,” the authors write. “We still do not fully comprehend the origin and development of routine electromagnetic fields in galaxies and how this field is maintained.”
The yellow regions reveal polarization disagreement in between the design and the data in this image from the study. Image Credit: West et al. 2021.
The team hopes a much better understanding of features like the tunnel will cause a better understanding of more far-off magnetic features. Filaments a lot more extensive than these exist, therefore do super-bubbles and bubbles. Astronomers have observed them in more distant areas of the Milky Way.
Studying these more distant functions is difficult. “Thus, it is likely that we do not presently have the resolution and level of sensitivity to see this level of structure in numerous areas other than the local environment and potentially in the Perseus arm,” the group concludes.
More:
“If we were to look up in the sky,” discusses West, “we would see this tunnel-like structure in simply about every direction we looked– that is, if we had eyes that might see radio light.”
West says shes been thinking about the pair of functions for 15 years since she initially saw a radio map of the sky. In current years shes developed a computer model that shows what the radio sky would look like from Earth as she altered the shape and location of the long radio ropes.” A few years ago, one of our co-authors, Tom Landecker, told me about a paper from 1965, from the early days of radio astronomy,” West said. These radio data are revealed projected as they would be seen in the sky together with the brightest stars and constellations outlines and constellation names overlaid.
Like this: Like Loading …