The Global Position System (GPS) has actually remained in usage for decades at this moment and forms the backbone of everything from vehicles automated driving systems to running watches. It has some weak points. Considering that the system is so well understood, it has been vulnerable to attacks, which have triggered problems varying from overriding the flight path of civilian and military drones to pirating the auto-pilot function of Teslas vehicles..
A group of researchers from the Ohio State University (OSU) and the University of California Irvine (UCI) has actually established a way to use Starlinks networked satellites as a fundamental navigation tool.
Starlink keeps growing, therefore do its capabilities. Recently, even individuals outside of SpaceX have even been developing abilities for it. A team of scientists from the Ohio State University (OSU) and the University of California Irvine (UCI) has actually developed a way to utilize Starlinks networked satellites as a standard navigation tool.
Each of these satellites is likewise in a much lower orbit than existing GPS satellites, making them easier to interact with.
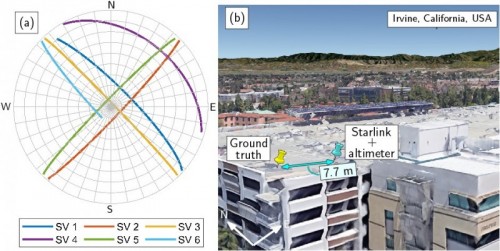
Using signal strength, metadata from the satellites themselves, and quotes of the orbital position of those satellites, researchers in Dr. Kassass lab were able to internationally pinpoint an antenna receiver within about 7.7 meters of its actual area.
The strategy made use of only 6 Starlink satellites for its positioning, and with the increasing number of satellites in orbit, Dr. Kassas expects that precision level to increase significantly.
If their precision increases to the expected level, then maybe Starlink, which was never meant as a navigational tool, can eventually fill in for GPS in a pinch.
In spite of being an important internet tool, Starlink has its drawbacks.
There are already alternatives to GPS, but Dr. Zak Kassas and his team decided to see if he could utilize a various technique that was never specifically meant for navigational purposes– Starlink. Currently, Starlink has approximately 1,700 satellites orbiting the Earth trying to offer broadband web throughout the world. SpaceX, the company responsible for the program, expects to release 40,000 satellites to support the network. Each of these satellites is also in a much lower orbit than existing GPS satellites, making them much easier to communicate with.
Starlink satellites also have recognizing metadata that permits ground controllers to distinguish in between signals coming from various satellites. Each satellite also has an unique orbital path that can be used as a positional reference. Utilizing signal strength, metadata from the satellites themselves, and price quotes of the orbital position of those satellites, scientists in Dr. Kassass lab were able to globally identify an antenna receiver within about 7.7 meters of its actual location.
Triangulation and test setup in Irvine, CACredit– Kassas et al
. This isnt rather the exact same accuracy level as GPS, which can vary between 0.3 and 5 meters in precision. Nevertheless, the technique used just six Starlink satellites for its positioning, and with the increasing variety of satellites in orbit, Dr. Kassas anticipates that accuracy level to increase drastically.
Nor is Starlink the only system the researchers have actually used this strategy on. Theyve used other low-Earth orbit satellite systems to find objects within 23 meters and even land-based transceivers to help find high-altitude aircraft.
Starlink satellites prepare for implementation. Credit: SpaceX.
Even more remarkably, the scientists did all this work with no help from SpaceX at all. They merely deciphered the metadata from each satellite, not the messages themselves, which hold encoded internet traffic. It does ask the question, how much more work would be needed to completely translate the messages rather than simply the metadata, consequently compromising Starlinks network integrity.
For now, the OSU/ UCI researchers have no intent to find out. Their work is focused totally on getting useful navigational data out of a brand-new facilities asset that wasnt developed for it. If their precision increases to the anticipated level, then possibly Starlink, which was never planned as a navigational tool, can eventually substitute GPS in a pinch.
Find out more: OSU– SpaceX satellite signals utilized like GPS to determine area on EarthIon– Exploiting Starlink Signals for Navigation: First ResultsArs Technica– Researchers usage Starlink satellites to identify area, comparable to GPSUT– How Will Starlinks Packet Routing Work?
Lead Image: Artist concept of Starlink constellation.Credit– Getty Images.
Like this: Like Loading …