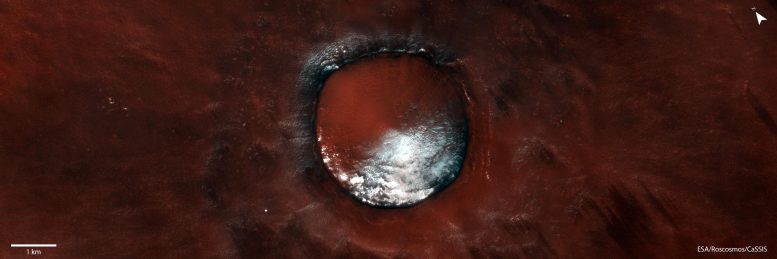
The dark material clearly noticeable on the crater rim– offering it a somewhat scorched appearance– most likely consists of volcanic materials such as basalt.
Credit: ESA/Roscosmos/CaSSIS, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO.
Many of the surrounding terrain is ice totally free, but has been formed by ongoing aeolian procedures. The streaks at the bottom right of the image are formed by winds that have actually removed the brighter iron oxide dust from the surface area, exposing a slightly darker underlying substrate.
TGO got to Mars in 2016 and started its complete science objective in 2018. The spacecraft is not just returning amazing images, but also offering the very best ever inventory of the planets atmospheric gases, and mapping the planets surface area for water-rich places. It will also provide information relay services for the 2nd ExoMars objective making up the Rosalind Franklin rover and Kazachok platform, when it gets here on Mars in 2023.
By European Space Firm (ESA).
December 30, 2021.
Credit: ESA/Roscosmos/CaSSIS, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO.
Like a spray of powdered sugar on an abundant red velour cake, this scene from the ESA/Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter records the contrasting colors of intense white water-ice against the rusty red martian soil.
This wonderful image was taken July 5, 2021, and soaks in the view of a 4 km-wide crater in Mars north polar region of Vastitas Borealis, centered at 70.6 ° N/230.3 ° E.
The crater is partly filled with water ice, which is likewise particularly predominant on its north-facing slopes that get fewer hours of sunshine on typical throughout the year.