Searching for sustainable options to animal-based proteins has actually been of growing interest within the food industry. Cellular farming, also called precision fermentation when used for recombinant component production, uses a biotechnology-based solution to decouple the production of animal proteins from animal farming by utilizing a microbial production system to produce the particular proteins rather.
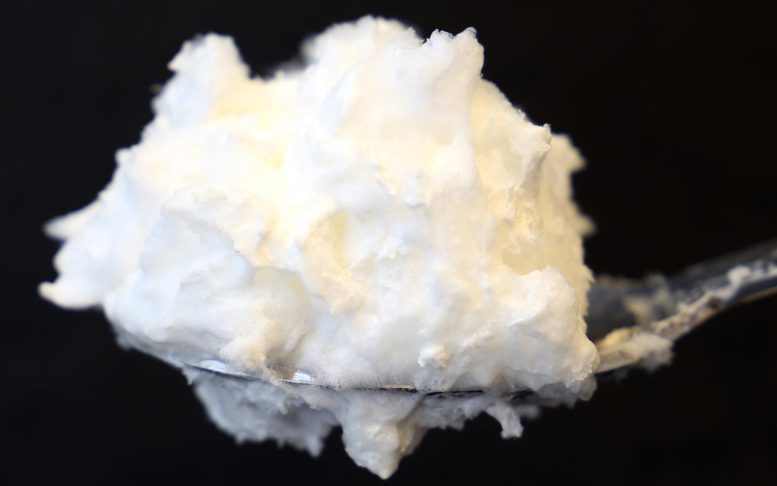
” For example, more than half of the egg white powder protein material is ovalbumin. The ovalbumin protein is then separated from the cells, concentrated, and dried to produce a last functional item,” says Dr. Emilia Nordlund from VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland.
Cell-cultured items generally need more electrical power than normal farming items, and therefore the kind of energy source utilized impacts the level of environmental effect. Nevertheless, the quantity of agricultural inputs required for ovalbumin production by microbes– such as glucose– is typically substantially lower per kilogram of protein powder.
” According to our research, this means that the fungus-produced ovalbumin reduced land usage requirements by nearly 90 percent and greenhouse gases by 31– 55 percent compared to the production of its chicken-based counterpart. In the future, when production is based upon low carbon energy, precision fermentation has the prospective to decrease the effect even by as much as 72 percent,” states Doctoral Researcher Natasha Järviö from the University of Helsinki.
For the impact of water utilize on the environment, the outcomes were less conclusive, revealing a high degree of dependency on the presumed location of the ovalbumin production website. In basic, the research study reveals the potential of the precision fermentation innovation to increase the sustainability of protein production, which can be even more increased by the use of low-carbon energy sources.
Referral: “Ovalbumin production utilizing Trichoderma reesei culture and low-carbon energy could alleviate the environmental impacts of chicken-egg-derived ovalbumin” by Natasha Järviö, Tuure Parviainen, Netta-Leena Maljanen, Yumi Kobayashi, Lauri Kujanpää, Dilek Ercili-Cura, Christopher P. Landowski, Toni Ryynänen, Emilia Nordlund and Hanna L. Tuomisto, 16 December 2021, Nature Food.DOI: 10.1038/ s43016-021-00418-2.
Parts of the egg white powder production chain, such as rearing chickens for egg production, generate large amounts of greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to water shortage, biodiversity loss, and deforestation.” For example, more than half of the egg white powder protein material is ovalbumin. The gene carrying the plans for ovalbumin is inserted by contemporary biotechnological tools into the fungi which then produces and secretes the very same protein that chickens produce. The ovalbumin protein is then separated from the cells, concentrated, and dried to create a last functional item,” states Dr. Emilia Nordlund from VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland.
Egg white protein produced by accuracy fermentation has outstanding foaming properties. Credit: VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland
The research study by the Future Sustainable Food Systems research group at the University of Helsinki together with VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland reveals that fungus-produced ovalbumin could have the potential to mitigate part of the ecological concern related to chicken egg white powder. When utilizing low carbon energy sources in the production, this is specifically real.
Chicken egg white powder is a typically utilized active ingredient in the food industry due to the premium protein it consists of. The yearly consumption of egg proteins in 2020 was around 1.6 million heaps and the market is expected to broaden further in the coming years.
The growing demand is raising questions about both sustainability and principles. Parts of the egg white powder production chain, such as rearing chickens for egg production, generate big amounts of greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to water deficiency, biodiversity loss, and logging. Additionally, extensive chicken farming has actually resulted in break outs of zoonotic illness by acting as a crucial tank for human pathogens.