The HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has actually recorded another beauty. This time the image shows water ice looking out from a cliffside on Mars. A layer of sediment obscures most of the ice, however fingers of it are noticeable.
Mars likely had ancient oceans, and the residues of all that water are concealed as ice. The image is from Mars Milankovic Crater, a popular effect crater that sits alone to the north of Olympus Mons, Mars tallest volcano, and the tallest volcano in the Solar System.
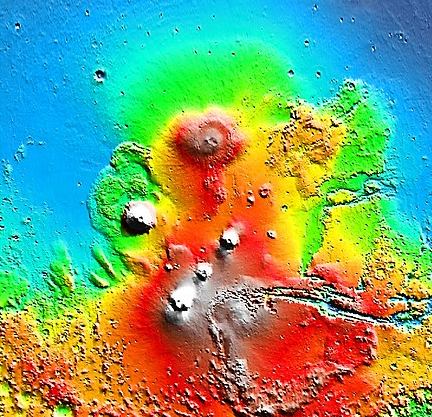
This topographical picture of Mars reveals the 3 volcanoes of Tharsis Montes, with Alba Mons to the north, and Olympus Mons to the northeast. Well above Olympus Mons is Milankovic crater, nearly alone in the flat plain of Vastitas Borealis. Image Credit: NASA.
Mars ancient oceans were relied on ice when Mars lost its atmosphere between about 3.7 billion to 4.2 billion years ago. The water now exists mostly as subsurface ice. A 2018 study found proof of a complex of liquid saltwater lakes under the south polar area, which created a lot of excitement. In 2019, researchers proposed that magma activity in the preceding one million years created enough heat to keep that water in liquid type. Then in 2021, another research study pointed out that the discovery of the subglacial polar lakes might be explained by other phenomena.
The presence of subglacial lakes of water on Mars will likely remain controversial for a long time. But the existence of subsurface water ice isnt controversial. Weve seen it.
When NASAs Phoenix Lander arrived on Mars in 2008 its retro-rockets exposed the shallow subsurface. Scientists think that the white spot is water ice. Image Credit: By NASA/Jet Propulsion Lab-Caltech/University of Arizona/Max Planck Institute– This image or video was catalogued by Jet Propulsion Laboratory of the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) under Photo ID: PIA10741., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4143566
Mars water exists as ice, locked into the worlds crust at varying depths, other than for the possibility of liquid water heated by magma existing under the polar area. Researchers believe that there are at least 5 million cubic kilometres of ice underground, with much more at depths beyond the capabilities of our present remote noticing instruments. Some of that ice is noticeable in the HiRISE image, looking out from under a layer of sediment.
The leading HiRISE image above is an infrared-red-blue image that highlights the presence of the ice. The RGB image below is more representative of what human eyes would see.
This image resembles more closely what the ice appears like to human eyes, but does not highlight the presence of the ice in addition to the IR image. Image Credit: NASA/JPL/UArizona
Weve improved our understanding of Martian water drastically in the last few years. A 2021 study showed that between 30% and 90% of Mars original water may be frozen under the surface, with large deposits in the Arcadia Planitia region. In 2019 NASA made a map of Martian water throughout the planets surface. NASA said that some of the water is only 30 cm (12 inches) deep, making it easily accessible to future explorers.
Its clear that mankind is reaching out to Mars. With our orbiters, landers, and rovers, were piecing together the worlds history. Mars was warm and once wet and may have harboured life. Future sample-return objectives might confirm the presence of microbial fossils. That would be a substantial discovery, worthy of all the fanfare it would no doubt produce.
However we want to set foot on Mars, at some point, in some way. And when that happens, our explorers will understand where to discover water.
More:
Mars likely had ancient oceans, and the remnants of all that water are concealed as ice. The image is from Mars Milankovic Crater, a popular effect crater that sits alone to the north of Olympus Mons, Mars highest volcano, and the highest volcano in the Solar System.
Mars ancient oceans were turned to ice when Mars lost its atmosphere between about 3.7 billion to 4.2 billion years earlier. Mars water exists as ice, locked into the planets crust at differing depths, other than for the possibility of liquid water heated by lava existing under the polar area. A 2021 study showed that between 30% and 90% of Mars original water might be frozen under the surface, with large deposits in the Arcadia Planitia region.
Like this: Like Loading …