
NASA is diligently working to restore the Hubble Space Telescope’s science operations after it entered safe mode on November 23, due to a malfunctioning gyroscope. (3D animation showing the Hubble Space Telescope over the Earth.) Credit: ESA/Hubble (M. Kornmesser & L. L. Christensen)
NASA is troubleshooting Hubble’s gyro issue to resume its science operations, ensuring its continued astronomical discoveries alongside telescopes like the James Webb.
NASA is working to resume science operations of the agency’s Hubble Space Telescope after it entered safe mode on November 23 due to an ongoing gyroscope (gyro) issue. Hubble’s instruments are stable, and the telescope is in good health.
The telescope automatically entered safe mode when one of its three gyroscopes gave faulty readings. The gyros measure the telescope’s turn rates and are part of the system that determines which direction the telescope is pointed. While in safe mode, science operations are suspended, and the telescope waits for new directions from the ground.
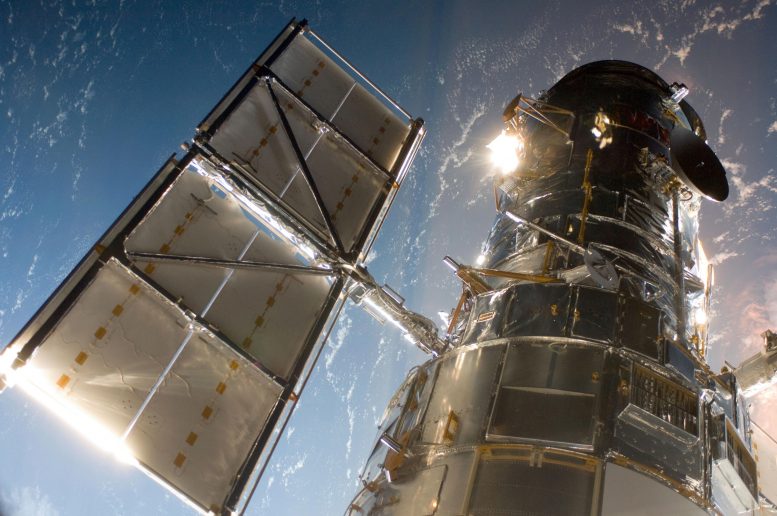


The Hubble Space Telescope was launched by the space shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990. Avoiding distortions of the atmosphere, Hubble has an unobstructed view peering to planets, stars, and galaxies, some more than 13.4 billion light-years away. Credit: NASA
Recent Challenges and Recovery Efforts
Hubble first entered safe mode on November 19. Although the operations team successfully recovered the spacecraft to resume observations the following day, the unstable gyro caused the observatory to suspend science operations once again on November 21. Following a successful recovery, Hubble entered safe mode again on November 23.
The team is now running tests to characterize the issue and develop solutions. If necessary, the spacecraft can be re-configured to operate with only one gyro. The spacecraft had six new gyros installed during the fifth and final space shuttle servicing mission in 2009. To date, three of those gyros remain operational, including the gyro currently experiencing fluctuations. Hubble uses three gyros to maximize efficiency, but could continue to make science observations with only one gyro if required.
Hubble’s Ongoing Legacy and Future Prospects
NASA anticipates Hubble will continue making groundbreaking discoveries, working with other observatories, such as the agency’s James Webb Space Telescope, throughout this decade and possibly into the next.
Launched in 1990, Hubble has been observing the universe for more than 33 years. Read more about some of Hubble’s greatest scientific discoveries.
